Social isolation linked to more severe COVID-19 outbreaks
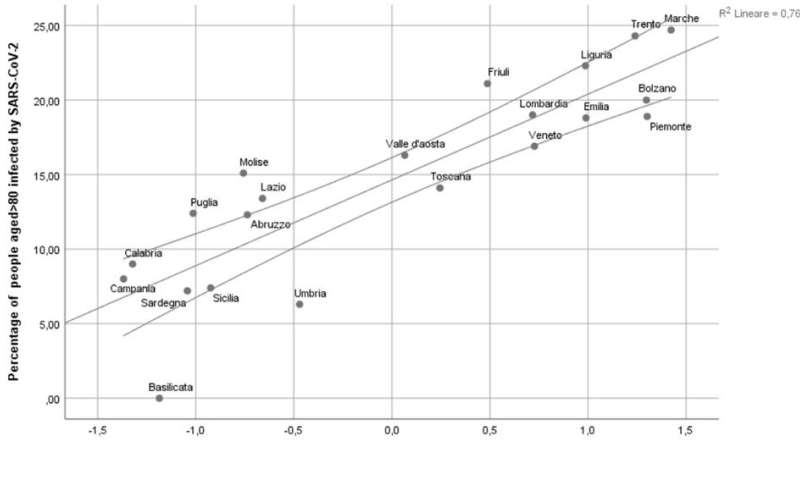
Regions of Italy with higher family fragmentation and a high number of residential nursing homes experienced the highest rate of COVID-19 infections in people over age 80, according to a new study published May 21, 2020 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Giuseppe Liotta of the University of Rome, Italy, and colleagues.
Italy has been one of the countries most affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. Researchers have speculated that this is due to Italy's age demographics as well as the connectedness of the older and younger generations and high rate of intergenerational contact. If true, this would suggest that regions with larger households would have more severe COVID-19 outbreaks in older adults.
In the new study, researchers used publicly available data published by each Italian administrative region as well as daily situation reports on COVID-19 published by the Italian Ministry of Health and spanning February 28 through March 31, 2020. All household and population data was extracted between April 1 and 7, 2020.
Across Italian regions, the COVID-19 incidence rate ranged from 0.27% to 4.09% of the population being affected. The mean number of household members ranged from 2.02 to 2.58; the percentage of one member households ranged from 28.5 to 40.9; and percentage of COVID-19 cases that occurred in people over age 80 ranged from 4.3 to 23.6. A model that reflected the percent of the population over age 80, days since 50 cases were registered, percentage of nursing home beds in the total population, and mean number of household members was best able to predict the COVID-19 incidence among older people in each region, with an adjusted R-squared value of 0.695 (p<0.001). A lower mean number of household members and higher number of nursing home beds was associated with more COVID-19 cases in older adults. The study was limited by the fact that age-specific infection rates were not available and the number of COVID-19 tests varied enormously by regions.
The authors add: "Variables associated with social isolation are risk factors forincrease in the proportion of cases in Italian patients aged >80 yearsamong the total number of cases." Professor Liotta also notes that "nursing homes bed rate is one of the determinants of SARS-CoV-2 infection rate among the individuals aged>80 in Italy."
Explore further








 User Center
User Center My Training Class
My Training Class Feedback
Feedback












Comments
Something to say?
Log in or Sign up for free