The farthest galaxy in the universe
A team of astronomers used the Keck I telescope to measure the distance to an ancient galaxy. They deduced the target galaxy GN-z11 is not only the oldest galaxy but also the most distant. It's so distant it defines the very boundary of the observable universe itself. The team hopes this study can shed light on a period of cosmological history when the universe was only a few hundred million years old.
We've all asked ourselves the big questions at times: "How big is the universe?" or "How and when did galaxies form?" Astronomers take these questions very seriously, and use fantastic tools that push the boundaries of technology to try and answer them. Professor Nobunari Kashikawa from the Department of Astronomy at the University of Tokyo is driven by his curiosity about galaxies. In particular, he sought the most distant one we can observe in order to find out how and when it came to be.
"From previous studies, the galaxy GN-z11 seems to be the farthest detectable galaxy from us, at 13.4 billion light years, or 134 nonillion kilometers (that's 134 followed by 30 zeros)," said Kashikawa. "But measuring and verifying such a distance is not an easy task."
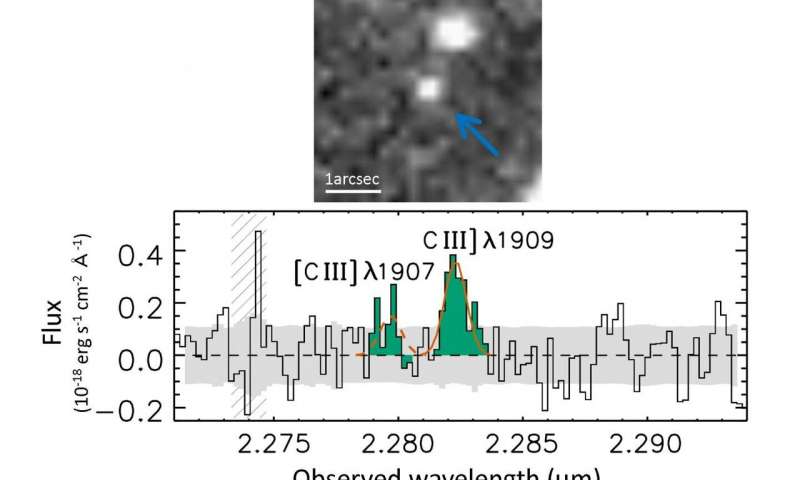
Kashikawa and his team measured what's known as the redshift of GN-z11; this refers to the way light stretches out, becomes redder, the farther it travels. Certain chemical signatures, called emission lines, imprint distinct patterns in the light from distant objects. By measuring how stretched these telltale signatures are, astronomers can deduce how far the light must have traveled, thus giving away the distance from the target galaxy.
"We looked at ultraviolet light specifically, as that is the area of the electromagnetic spectrum we expected to find the redshifted chemical signatures," said Kashikawa. "The Hubble Space Telescope detected the signature multiple times in the spectrum of GN-z11. However, even the Hubble cannot resolve ultraviolet emission lines to the degree we needed. So we turned to a more up-to-date ground-based spectrograph, an instrument to measure emission lines, called MOSFIRE, which is mounted to the Keck I telescope in Hawaii."
The MOSFIRE captured the emission lines from GN-z11 in detail, which allowed the team to make a much better estimation on its distance than was possible from previous data. When working with distances at these scales, it is not sensible to use our familiar units of kilometers or even multiples of them; instead, astronomers use a value known as the redshift number denoted by z. Kashikawa and his team improved the accuracy of the galaxy's z value by a factor of 100. If subsequent observations can confirm this, then the astronomers can confidently say GN-z11 is the farthest galaxy ever detected in the universe.
Explore further








 User Center
User Center My Training Class
My Training Class Feedback
Feedback












Comments
Something to say?
Log in or Sign up for free